没有前进
蜗牛的粘液achatina fulica对人软骨细胞具有积极作用
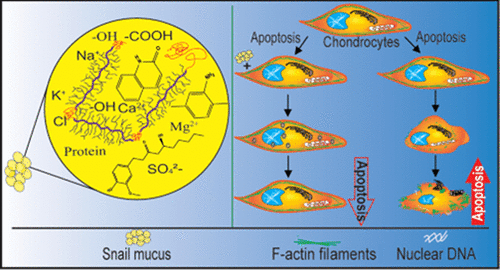
这项研究报告了 Achatina fulica 粘液作为骨关节炎和软骨组织体外修复的潜在治疗修复剂的新用途. 分离出蜗牛粘液, 已灭菌, 并使用 FTIR 进行表征, XPS, 流变学, 和 LC-MS/MS. GAG, 糖, 苯酚, 并使用标准测定法估算蛋白质含量. The LC–MS/MS identified 6-gingerol and some other small molecules. The effects of the sterilized mucus were studied on human chondrocytes using the C28/I2 cell as a model for the in vitro assays. The MTT assay indicates that mucus extracted from the pedal of A. fulica is biocompatible with the cells up to a concentration of 50 μg/mL. The mucus promoted cell migration and proliferation and completely closed the wound within 72 h, as indicated in the in vitro scratch assay. In addition, the snail mucus reduced apoptosis significantly (p < 0.05) in the treated cells by 74.6%. It preserved the cytoskeletal integrity of the C28/I2 cells, attributed mainly to GAGs and 6-gingerol content of the mucus. In conclusion, this present study suggests that GAGs and 6-gingerol conferred wound-healing and antiapoptotic properties on the mucus secretion from A. fulica and can be explored for therapeutic repair and cartilage tissue engineering.
Victor A. and Ashok M. Raichur